
Disclaimer: Please note this article is not financial advice. The purpose of our blog is purely educational, so please consult a professional accountant or financial advisor before making any financial decision.
The revenue from e-commerce retail sales in Canada has seen an upward trend since 2017. According to Statista, from $28.59 billion in 2017, it rose to $62.12 billion in 2023. The data company forecasts this upward trend to continue until 2027, with predicted revenue of $94.14 billion.
Behind these numbers are millions of eCommerce sellers like you who have ventured into the industry and opened businesses to fellow Canadians and customers worldwide. If you just began selling online, you have plenty of tasks on your plate, but one thing you should prioritize is taxation.
Let us help you make your workload lighter by providing you with knowledge about Canada's online sales tax for businesses.
To avoid getting lost, familiarize yourself with the different terms for Canadian taxes. You need to remember four: Goods and Services Tax (GST), Provincial Sales Tax (PST), Harmonized Sales Tax (HST), and Quebec Sales Tax (QST). Let's check their definitions one by one.
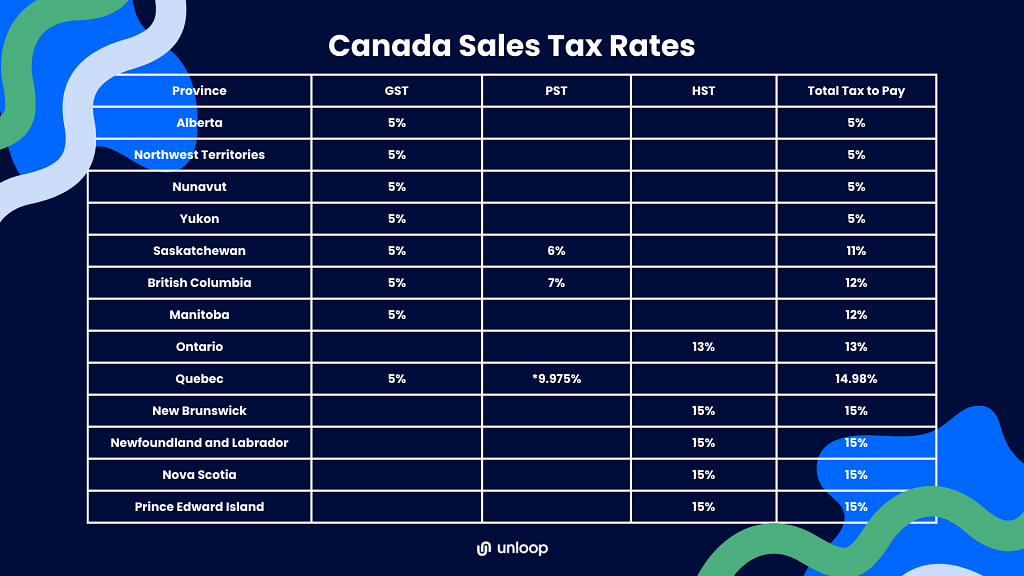
The Canadian government mandates a federal tax called the GST which it levies upon all states. The GST comes at 5% of the sale price. The rate will still increase when PST or QST is added. GST is applied to almost all products sold in physical stores and online. Only those tagged as zero-rate are exempted from this taxation.
If your buyers are from Alberta, British Columbia, Manitoba, Northwest Territories, Nunavut, Saskatchewan, Quebec, and Yukon, prepare to charge this sales tax. All these provinces have GST either independently or together with PST or QST.
The provincial sales tax, on the other hand, is a local sales tax working in combination with the GST. For example, if the GST is 5% and the PST is 7%, the Canada Revenue Agency (CRA) charges businesses a 12% sales tax. However, not all provinces have a PST. Some provinces charge only GST, while others apply the Harmonized Sales Tax (HST).
As the name suggests, this is the additional tax imposed by provinces like British Columbia, Manitoba, and Saskatchewan. The tax rate varies per province.
So when computing the sales tax, adding the 5% GST to the given PST rates results in the following final rates:
An example transaction goes like this: let's say you sold a pair of rubber shoes at $29.99 to a customer living in British Columbia. For this sale, you have to charge a 12% sales tax.
In place of the GST and PST, certain provinces opt for a harmonized sales tax. Aside from Ontario, participating provinces follow the same HST rate, which is a standard 15%, while Ontario uses 13%.
Lawmakers have passed the harmonization of the two through HST to skip the hassle of separately computing federal and provincial taxes. When you make sales from these provinces, you do not need to look for the GST and PST rates; apply the HST rate.
Five provinces, New Brunswick, Newfoundland and Labrador, Nova Scotia, Ontario, and Prince Edward Island, follow this taxation system, and the rates vary per province.
Quebec's PST is called the QST. Quebec is the only province to differ among all provinces that use PST with a sales tax rate of 9.975%.
In Quebec, the sales tax consists of the GST and QST, with the QST at 9.975% and GST still at 5%. However, you do not have to remit QST if you satisfy any of the following conditions:
For instance, a supplier that does not reside and does not have a physical store in Quebec supplies products to Quebec businesses. In this case, they should only charge their customers with the 5% GST. On the other hand, sellers must charge GST and QST for individual orders delivered to Quebec residents.

Whether you are a new resident, a maple leaf-loving local, self-employed, or a business entity, understanding your tax obligations is crucial to maintain compliance with the Canadian tax system. In Canada, here are the businesses that need to pay taxes.
Canadian businesses follow the “small supplier rule.” In this rule, if you qualify as a small business that makes less than $30,000 in annual revenue on taxable supplies, you're not required to open a GST/HST account. Collecting and remitting sales taxes is unnecessary for you.
However, most provinces under PST don't cover provincial sales taxes for small suppliers, so while you don't have to pay GST or HST, you might still have to pay the provincial portion regardless of your sales volume.
Originally, the federal government did not require businesses not physically based in Canada to collect and remit Canadian sales taxes. However, new tax policies put Canadian businesses at a disadvantage since their prices would be higher.
Because of this, currently, foreign businesses must pay the GST/HST rate and the PST if their total revenue surpasses $30,000. Foreign businesses or non-residents are not required to be physically present in Canada. They must voluntarily register with the CRA and provide personal solutions to determine where their customers live and what taxes apply to their purchases.
Taxation is undeniably complex, and the different sales taxes in Canada make it more overwhelming. With that, here are some reminders to help you know how much to pass on to your client or whether to charge them or not.
You must also know the department where you must submit your collected sales tax. So, keep reading!
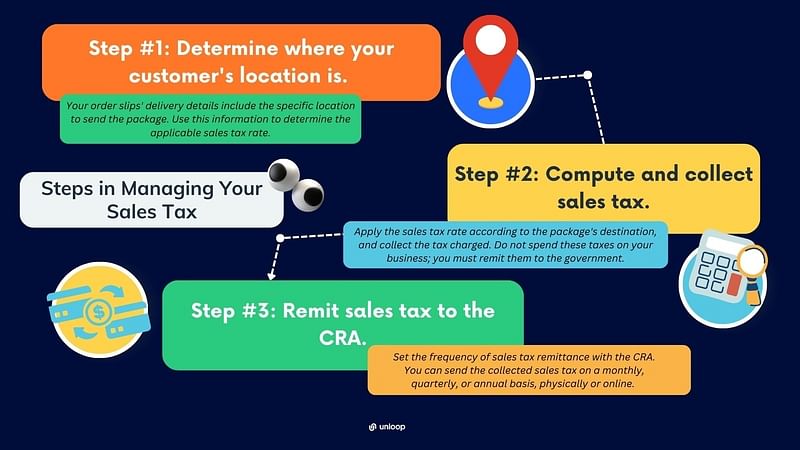
The first step is to determine the buyer's address. Remember that the basis of sales tax is not where the package came from but where it is going. For instance, an order from Ontario will be delivered to a customer in Manitoba. The sales tax rate to follow is Manitoba's 12% sales tax rate.
The standard procedure in British Columbia, Manitoba, and Saskatchewan is that orders sent to residents of these provinces should be taxed accordingly. However, specific rules differ on who should pay taxes and who is exempted. If you deliver in these locations, it is best to get into the specifics of the local tax regulations.
While almost all goods have sales tax and most individuals must pay taxes for their purchases, some products are zero-rated and customers tax exempted.
These are the goods you can buy without paying any sales tax.
These specific groups are also not required to pay sales taxes.
Remember not to apply sales tax if you sell these goods or to these groups.
For individual orders, sales tax is based on the location of the buyer. But what if you are a raw materials manufacturer and sell not to end users but to product developers? Should you also charge sales tax to your customers?
The levels of resales are a common scenario in the production of goods. A resale certificate will save the business buying your raw materials from paying sales tax as they are not the end user of the final product.

In Canada, Internet sales tax regulations state that online sellers are required to charge sales tax on their orders. With that, there is no confusion about whether you should collect taxes from your buyers.
Whether selling in a mall, a stand-alone boutique, or online, sales tax applies if you made a taxable sale to a Canadian customer. However, as mentioned earlier, it's best to understand and abide by the specific ecommerce sales tax rules per province.
In Canada, you should be familiar with these two offices to pay your taxes: Revenu Quebec for the province of Quebec and the Canadian Revenue Agency (CRA) for the rest of the country.
These two offices implement tax laws and handle all tax-related transactions, from income tax, value-added tax, and excise tax to sales tax. After collecting the sales tax, you need to remit all the sales tax you collected to these agencies.
Managing sales tax in Canada involves several crucial steps to ensure compliance and smooth operations. From understanding the different tax rates in various jurisdictions to computing, collecting, and remitting taxes, this guide outlines essential steps to navigate the complexities of Canadian sales tax.
Tax time can be stressful for business owners since calculating and filing taxes can get very complicated. Fortunately, the Canada Revenue Agency has provided three easy ways to pay your sales taxes.
Nowadays, it's becoming less popular to go to the bank for all your transactions physically. Different financial institutions are normalizing electronic payment methods, and it's also become a reliable payment method for the Canada Revenue Agency.
The Canada Revenue Agency devised an online payment system called MyPayment. Check the CRA's website to see the specific guidelines for MyPayment.
Despite the rising popularity of electronic payments, bank runs aren't going out of style yet. To pay through financial institutions, fill up a form called “Form RC158 - Remittance Voucher,” which you can only get from the bank since no soft copies are available online.
Should you need to make other tax-related payments, financial institutions also provide the following forms:
If you plan on paying with foreign currency, you'll have to apply the current exchange rate to your remittance and pay that.
If the other two payment options don't work, you can always go old school and remit your sales taxes through snail mail. The Canada Revenue Agency can accept payments via mail or courier, but you'll have to keep the amount below $50,000.
Otherwise, you'll have to pay either electronically or through a bank.

Taxes are every business's responsibility; staying in business means paying taxes without error. Not filing your taxes or even filing them improperly, like miscalculating or failing to declare some expenses, could lead to serious repercussions for your business. It could lead to legal battles and, in serious cases, jail time.
Here are a few examples of tax crimes all businesses should be wary of.
Generally speaking, tax evasion is failure to pay taxes. The worst businesses intentionally commit tax evasion by undervaluing their taxable assets or not reporting taxes at all. You can get more jail time from tax evasion than tax fraud.
Tax fraud, on the other hand, is simply misreporting your taxable assets. Sometimes, people confuse which assets are taxable and allow themselves to be willfully blind to avoid reporting such assets. Assisting people in committing these acts is also considered tax fraud.
You can do your sales tax on your own if you are still beginning your business, but you can imagine the increase in the workload when your sales boom. Ecommerce sales tax solutions make your business processes more efficient and lessen your work.
Having a team of experts looking at your tax returns is important so you won't make any mistakes regarding your taxes. Here are the ways to make sales tax management easier.
Rely on sales tax software like QuickBooks, Xero, A2X, and Hubdoc. They collate sales transaction details and compute sales tax per order. They also store all transactions in the system, so you can run reports to check how much sales tax you've collected and other key performance indicators to help you make decisions.
Delegate bookkeeping to a trained bookkeeper to ensure the proper tracking and categorizing all transactions. An experienced bookkeeper will update your books timely and ensure data accuracy while you focus on business operations, product quality checks, and customer service.
Taxation is an essential task that can determine your business's success or failure. Thus, it is best to have someone well-versed in tax laws and regulations like an ecommerce sales tax accountant. Your accountant will check your sales tax compliance and create reports from the information gathered by the bookkeeper. Let them take care of tax management and payment on your business too.
As a business owner, you are now one of the millions of Canadian ecommerce sellers contributing to the growth of the industry in the country and worldwide. You can be a responsible seller by collecting the correct sales taxes as mandated by the Canadian government and remitting them on time. If you ever need assistance in this area of your business, we at Unloop offer bookkeeping business solutions. Our team of experienced bookkeepers will help you track and prepare your sales tax information before tax season. Delegate the task to us so that you can focus on scaling your business. Book a call with us now. We'd love to hear from you!
Unloop is the first and only accounting firm exclusively servicing ecommerce and inventory businesses in the US and Canada. With the power of people and technology, our team dives deep into COGS and inventory accounting. You are paired with a dedicated bookkeeping team that prepares accurate financial statements, financial forecasts, and can also pay bills or run payroll for you. Come tax time, everything is organized and ready to go, so you don't need to worry. Book a call with an ecommerce accountant today to learn more.